python爬虫请求库httpx和parsel解析库的使用测评
Python网络爬虫领域两个最新的比较火的工具莫过于httpx和parsel了。httpx号称下一代的新一代的网络请求库,不仅支持requests库的所有操作,还能发送异步请求,为编写异步爬虫提供了便利。parsel最初集成在著名Python爬虫框架Scrapy中,后独立出来成立一个单独的模块,支持XPath选择器, CSS选择器和正则表达式等多种解析提取方式, 据说相比于BeautifulSoup,parsel的解析效率更高。
今天我们就以爬取链家网上的二手房在售房产信息为例,来测评下httpx和parsel这两个库。为了节约时间,我们以爬取上海市浦东新区500万元-800万元以上的房产为例。
requests + BeautifulSoup组合
首先上场的是Requests + BeautifulSoup组合,这也是大多数人刚学习Python爬虫时使用的组合。本例中爬虫的入口url是https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/a3p5/, 先发送请求获取最大页数,然后循环发送请求解析单个页面提取我们所要的信息(比如小区名,楼层,朝向,总价,单价等信息),最后导出csv文件。如果你正在阅读本文,相信你对Python爬虫已经有了一定了解,所以我们不会详细解释每一行代码。
整个项目代码如下所示:
# homelink_requests.py
# Author: 大江狗
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import re
import time
class HomeLinkSpider(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ua = UserAgent()
self.headers = {"User-Agent": self.ua.random}
self.data = list()
self.path = "浦东_三房_500_800万.csv"
self.url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/a3p5/"
def get_max_page(self):
response = requests.get(self.url, headers=self.headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
a = soup.select('div[class="page-box house-lst-page-box"]')
#使用eval是字符串转化为字典格式
max_page = eval(a[0].attrs["page-data"])["totalPage"]
return max_page
else:
print("请求失败 status:{}".format(response.status_code))
return None
def parse_page(self):
max_page = self.get_max_page()
for i in range(1, max_page + 1):
url = 'https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg{}a3p5/'.format(i)
response = requests.get(url, headers=self.headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
ul = soup.find_all("ul", class_="sellListContent")
li_list = ul[0].select("li")
for li in li_list:
detail = dict()
detail['title'] = li.select('div[class="title"]')[0].get_text()
# 2室1厅 | 74.14平米 | 南 | 精装 | 高楼层(共6层) | 1999年建 | 板楼
house_info = li.select('div[class="houseInfo"]')[0].get_text()
house_info_list = house_info.split(" | ")
detail['bedroom'] = house_info_list[0]
detail['area'] = house_info_list[1]
detail['direction'] = house_info_list[2]
floor_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{1,2}')
# 从字符串任意位置匹配
match1 = re.search(floor_pattern, house_info_list[4])
if match1:
detail['floor'] = match1.group()
else:
detail['floor'] = "未知"
# 匹配年份
year_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{4}')
match2 = re.search(year_pattern, house_info_list[5])
if match2:
detail['year'] = match2.group()
else:
detail['year'] = "未知"
# 文兰小区 - 塘桥, 提取小区名和哈快
position_info = li.select('div[class="positionInfo"]')[0].get_text().split(' - ')
detail['house'] = position_info[0]
detail['location'] = position_info[1]
# 650万,匹配650
price_pattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
total_price = li.select('div[class="totalPrice"]')[0].get_text()
detail['total_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, total_price).group()
# 单价64182元/平米, 匹配64182
unit_price = li.select('div[class="unitPrice"]')[0].get_text()
detail['unit_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, unit_price).group()
self.data.append(detail)
def write_csv_file(self):
head = ["标题", "小区", "房厅", "面积", "朝向", "楼层", "年份",
"位置", "总价(万)", "单价(元/平方米)"]
keys = ["title", "house", "bedroom", "area", "direction",
"floor", "year", "location",
"total_price", "unit_price"]
try:
with open(self.path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf_8_sig') as csv_file:
writer = csv.writer(csv_file, dialect='excel')
if head is not None:
writer.writerow(head)
for item in self.data:
row_data = []
for k in keys:
row_data.append(item[k])
# print(row_data)
writer.writerow(row_data)
print("Write a CSV file to path %s Successful." % self.path)
except Exception as e:
print("Fail to write CSV to path: %s, Case: %s" % (self.path, e))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
home_link_spider = HomeLinkSpider()
home_link_spider.parse_page()
home_link_spider.write_csv_file()
end = time.time()
print("耗时:{}秒".format(end-start))
注意:我们使用了fake_useragent, requests和BeautifulSoup,这些都需要通过pip事先安装好才能用。
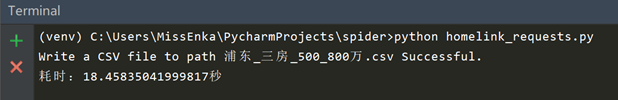
现在我们来看下爬取结果,耗时约18.5秒,总共爬取580条数据。
requests + parsel组合
这次我们同样采用requests获取目标网页内容,使用parsel库(事先需通过pip安装)来解析。Parsel库的用法和BeautifulSoup相似,都是先创建实例,然后使用各种选择器提取DOM元素和数据,但语法上稍有不同。Beautiful有自己的语法规则,而Parsel库支持标准的css选择器和xpath选择器, 通过get方法或getall方法获取文本或属性值,使用起来更方便。
# BeautifulSoup的用法
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
ul = soup.find_all("ul", class_="sellListContent")[0]
# Parsel的用法, 使用Selector类
from parsel import Selector
selector = Selector(response.text)
ul = selector.css('ul.sellListContent')[0]
# Parsel获取文本值或属性值案例
selector.css('div.title span::text').get()
selector.css('ul li a::attr(href)').get()
>>> for li in selector.css('ul > li'):
... print(li.xpath('.//@href').get())
注:老版的parsel库使用extract()或extract_first()方法获取文本或属性值,在新版中已被get()和getall()方法替代。
全部代码如下所示:
# homelink_parsel.py
# Author: 大江狗
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import requests
import csv
import re
import time
from parsel import Selector
class HomeLinkSpider(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ua = UserAgent()
self.headers = {"User-Agent": self.ua.random}
self.data = list()
self.path = "浦东_三房_500_800万.csv"
self.url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/a3p5/"
def get_max_page(self):
response = requests.get(self.url, headers=self.headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
# 创建Selector类实例
selector = Selector(response.text)
# 采用css选择器获取最大页码div Boxl
a = selector.css('div[class="page-box house-lst-page-box"]')
# 使用eval将page-data的json字符串转化为字典格式
max_page = eval(a[0].xpath('//@page-data').get())["totalPage"]
print("最大页码数:{}".format(max_page))
return max_page
else:
print("请求失败 status:{}".format(response.status_code))
return None
def parse_page(self):
max_page = self.get_max_page()
for i in range(1, max_page + 1):
url = 'https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg{}a3p5/'.format(i)
response = requests.get(url, headers=self.headers)
selector = Selector(response.text)
ul = selector.css('ul.sellListContent')[0]
li_list = ul.css('li')
for li in li_list:
detail = dict()
detail['title'] = li.css('div.title a::text').get()
# 2室1厅 | 74.14平米 | 南 | 精装 | 高楼层(共6层) | 1999年建 | 板楼
house_info = li.css('div.houseInfo::text').get()
house_info_list = house_info.split(" | ")
detail['bedroom'] = house_info_list[0]
detail['area'] = house_info_list[1]
detail['direction'] = house_info_list[2]
floor_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{1,2}')
match1 = re.search(floor_pattern, house_info_list[4]) # 从字符串任意位置匹配
if match1:
detail['floor'] = match1.group()
else:
detail['floor'] = "未知"
# 匹配年份
year_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{4}')
match2 = re.search(year_pattern, house_info_list[5])
if match2:
detail['year'] = match2.group()
else:
detail['year'] = "未知"
# 文兰小区 - 塘桥 提取小区名和哈快
position_info = li.css('div.positionInfo a::text').getall()
detail['house'] = position_info[0]
detail['location'] = position_info[1]
# 650万,匹配650
price_pattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
total_price = li.css('div.totalPrice span::text').get()
detail['total_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, total_price).group()
# 单价64182元/平米, 匹配64182
unit_price = li.css('div.unitPrice span::text').get()
detail['unit_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, unit_price).group()
self.data.append(detail)
def write_csv_file(self):
head = ["标题", "小区", "房厅", "面积", "朝向", "楼层",
"年份", "位置", "总价(万)", "单价(元/平方米)"]
keys = ["title", "house", "bedroom", "area",
"direction", "floor", "year", "location",
"total_price", "unit_price"]
try:
with open(self.path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf_8_sig') as csv_file:
writer = csv.writer(csv_file, dialect='excel')
if head is not None:
writer.writerow(head)
for item in self.data:
row_data = []
for k in keys:
row_data.append(item[k])
# print(row_data)
writer.writerow(row_data)
print("Write a CSV file to path %s Successful." % self.path)
except Exception as e:
print("Fail to write CSV to path: %s, Case: %s" % (self.path, e))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
home_link_spider = HomeLinkSpider()
home_link_spider.parse_page()
home_link_spider.write_csv_file()
end = time.time()
print("耗时:{}秒".format(end-start))
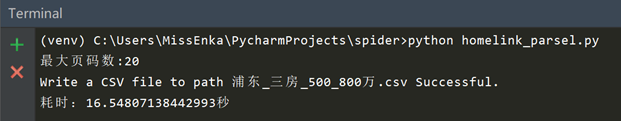
现在我们来看下爬取结果,爬取580条数据耗时约16.5秒,节省了2秒时间。可见parsel比BeautifulSoup解析效率是要高的,爬取任务少时差别不大,任务多的话差别可能会大些。
httpx同步 + parsel组合
我们现在来更进一步,使用httpx替代requests库。httpx发送同步请求的方式和requests库基本一样,所以我们只需要修改上例中两行代码,把requests替换成httpx即可, 其余代码一模一样。
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import csv
import re
import time
from parsel import Selector
import httpx
class HomeLinkSpider(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ua = UserAgent()
self.headers = {"User-Agent": self.ua.random}
self.data = list()
self.path = "浦东_三房_500_800万.csv"
self.url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/a3p5/"
def get_max_page(self):
# 修改这里把requests换成httpx
response = httpx.get(self.url, headers=self.headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
# 创建Selector类实例
selector = Selector(response.text)
# 采用css选择器获取最大页码div Boxl
a = selector.css('div[class="page-box house-lst-page-box"]')
# 使用eval将page-data的json字符串转化为字典格式
max_page = eval(a[0].xpath('//@page-data').get())["totalPage"]
print("最大页码数:{}".format(max_page))
return max_page
else:
print("请求失败 status:{}".format(response.status_code))
return None
def parse_page(self):
max_page = self.get_max_page()
for i in range(1, max_page + 1):
url = 'https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg{}a3p5/'.format(i)
# 修改这里把requests换成httpx
response = httpx.get(url, headers=self.headers)
selector = Selector(response.text)
ul = selector.css('ul.sellListContent')[0]
li_list = ul.css('li')
for li in li_list:
detail = dict()
detail['title'] = li.css('div.title a::text').get()
# 2室1厅 | 74.14平米 | 南 | 精装 | 高楼层(共6层) | 1999年建 | 板楼
house_info = li.css('div.houseInfo::text').get()
house_info_list = house_info.split(" | ")
detail['bedroom'] = house_info_list[0]
detail['area'] = house_info_list[1]
detail['direction'] = house_info_list[2]
floor_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{1,2}')
match1 = re.search(floor_pattern, house_info_list[4]) # 从字符串任意位置匹配
if match1:
detail['floor'] = match1.group()
else:
detail['floor'] = "未知"
# 匹配年份
year_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{4}')
match2 = re.search(year_pattern, house_info_list[5])
if match2:
detail['year'] = match2.group()
else:
detail['year'] = "未知"
# 文兰小区 - 塘桥 提取小区名和哈快
position_info = li.css('div.positionInfo a::text').getall()
detail['house'] = position_info[0]
detail['location'] = position_info[1]
# 650万,匹配650
price_pattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
total_price = li.css('div.totalPrice span::text').get()
detail['total_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, total_price).group()
# 单价64182元/平米, 匹配64182
unit_price = li.css('div.unitPrice span::text').get()
detail['unit_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, unit_price).group()
self.data.append(detail)
def write_csv_file(self):
head = ["标题", "小区", "房厅", "面积", "朝向", "楼层",
"年份", "位置", "总价(万)", "单价(元/平方米)"]
keys = ["title", "house", "bedroom", "area", "direction",
"floor", "year", "location",
"total_price", "unit_price"]
try:
with open(self.path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf_8_sig') as csv_file:
writer = csv.writer(csv_file, dialect='excel')
if head is not None:
writer.writerow(head)
for item in self.data:
row_data = []
for k in keys:
row_data.append(item[k])
# print(row_data)
writer.writerow(row_data)
print("Write a CSV file to path %s Successful." % self.path)
except Exception as e:
print("Fail to write CSV to path: %s, Case: %s" % (self.path, e))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
home_link_spider = HomeLinkSpider()
home_link_spider.parse_page()
home_link_spider.write_csv_file()
end = time.time()
print("耗时:{}秒".format(end-start))
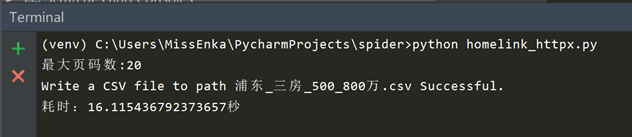
整个爬取过程耗时16.1秒,可见使用httpx发送同步请求时效率和requests基本无差别。
注意:Windows上使用pip安装httpx可能会出现报错,要求安装Visual Studio C++, 这个下载安装好就没事了。
接下来,我们就要开始王炸了,使用httpx和asyncio编写一个异步爬虫看看从链家网上爬取580条数据到底需要多长时间。
httpx异步+ parsel组合
Httpx厉害的地方就是能发送异步请求。整个异步爬虫实现原理时,先发送同步请求获取最大页码,把每个单页的爬取和数据解析变为一个asyncio协程任务(使用async定义),最后使用loop执行。
大部分代码与同步爬虫相同,主要变动地方有两个:
# 异步 - 使用协程函数解析单页面,需传入单页面url地址
async def parse_single_page(self, url):
# 使用httpx发送异步请求获取单页数据
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(url, headers=self.headers)
selector = Selector(response.text)
# 其余地方一样
def parse_page(self):
max_page = self.get_max_page()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
# Python 3.6之前用ayncio.ensure_future或loop.create_task方法创建单个协程任务
# Python 3.7以后可以用户asyncio.create_task方法创建单个协程任务
tasks = []
for i in range(1, max_page + 1):
url = 'https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg{}a3p5/'.format(i)
tasks.append(self.parse_single_page(url))
# 还可以使用asyncio.gather(*tasks)命令将多个协程任务加入到事件循环
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
loop.close()
整个项目代码如下所示:
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
import csv
import re
import time
from parsel import Selector
import httpx
import asyncio
class HomeLinkSpider(object):
def __init__(self):
self.ua = UserAgent()
self.headers = {"User-Agent": self.ua.random}
self.data = list()
self.path = "浦东_三房_500_800万.csv"
self.url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/a3p5/"
def get_max_page(self):
response = httpx.get(self.url, headers=self.headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
# 创建Selector类实例
selector = Selector(response.text)
# 采用css选择器获取最大页码div Boxl
a = selector.css('div[class="page-box house-lst-page-box"]')
# 使用eval将page-data的json字符串转化为字典格式
max_page = eval(a[0].xpath('//@page-data').get())["totalPage"]
print("最大页码数:{}".format(max_page))
return max_page
else:
print("请求失败 status:{}".format(response.status_code))
return None
# 异步 - 使用协程函数解析单页面,需传入单页面url地址
async def parse_single_page(self, url):
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(url, headers=self.headers)
selector = Selector(response.text)
ul = selector.css('ul.sellListContent')[0]
li_list = ul.css('li')
for li in li_list:
detail = dict()
detail['title'] = li.css('div.title a::text').get()
# 2室1厅 | 74.14平米 | 南 | 精装 | 高楼层(共6层) | 1999年建 | 板楼
house_info = li.css('div.houseInfo::text').get()
house_info_list = house_info.split(" | ")
detail['bedroom'] = house_info_list[0]
detail['area'] = house_info_list[1]
detail['direction'] = house_info_list[2]
floor_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{1,2}')
match1 = re.search(floor_pattern, house_info_list[4]) # 从字符串任意位置匹配
if match1:
detail['floor'] = match1.group()
else:
detail['floor'] = "未知"
# 匹配年份
year_pattern = re.compile(r'\d{4}')
match2 = re.search(year_pattern, house_info_list[5])
if match2:
detail['year'] = match2.group()
else:
detail['year'] = "未知"
# 文兰小区 - 塘桥 提取小区名和哈快
position_info = li.css('div.positionInfo a::text').getall()
detail['house'] = position_info[0]
detail['location'] = position_info[1]
# 650万,匹配650
price_pattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
total_price = li.css('div.totalPrice span::text').get()
detail['total_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, total_price).group()
# 单价64182元/平米, 匹配64182
unit_price = li.css('div.unitPrice span::text').get()
detail['unit_price'] = re.search(price_pattern, unit_price).group()
self.data.append(detail)
def parse_page(self):
max_page = self.get_max_page()
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
# Python 3.6之前用ayncio.ensure_future或loop.create_task方法创建单个协程任务
# Python 3.7以后可以用户asyncio.create_task方法创建单个协程任务
tasks = []
for i in range(1, max_page + 1):
url = 'https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg{}a3p5/'.format(i)
tasks.append(self.parse_single_page(url))
# 还可以使用asyncio.gather(*tasks)命令将多个协程任务加入到事件循环
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
loop.close()
def write_csv_file(self):
head = ["标题", "小区", "房厅", "面积", "朝向", "楼层",
"年份", "位置", "总价(万)", "单价(元/平方米)"]
keys = ["title", "house", "bedroom", "area", "direction",
"floor", "year", "location",
"total_price", "unit_price"]
try:
with open(self.path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf_8_sig') as csv_file:
writer = csv.writer(csv_file, dialect='excel')
if head is not None:
writer.writerow(head)
for item in self.data:
row_data = []
for k in keys:
row_data.append(item[k])
writer.writerow(row_data)
print("Write a CSV file to path %s Successful." % self.path)
except Exception as e:
print("Fail to write CSV to path: %s, Case: %s" % (self.path, e))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start = time.time()
home_link_spider = HomeLinkSpider()
home_link_spider.parse_page()
home_link_spider.write_csv_file()
end = time.time()
print("耗时:{}秒".format(end-start))
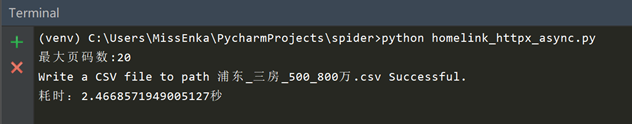
现在到了见证奇迹的时刻了。从链家网上爬取了580条数据,使用httpx编写的异步爬虫仅仅花了2.5秒!!
对比与总结
爬取同样的内容,采用不同工具组合耗时是不一样的。httpx异步+parsel组合毫无疑问是最大的赢家, requests和BeautifulSoup确实可以功成身退啦。
- requests + BeautifulSoup: 18.5 秒
- requests + parsel: 16.5秒
- httpx 同步 + parsel: 16.1秒
- httpx 异步 + parsel: 2.5秒
对于Python爬虫,你还有喜欢的库吗?
以上就是python爬虫请求库httpx和parsel解析库的使用测评的详细内容,更多关于python httpx和parsel的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
相关文章

详解Python利用configparser对配置文件进行读写操作
这篇文章主要介绍了详解Python利用configparser对配置文件进行读写操作,本文通过实例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2020-11-11
解决python 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认驱动程序的问题
今天小编就为大家分享一篇解决python 未发现数据源名称并且未指定默认驱动程序的问题,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。一起跟随小编过来看看吧2018-12-12
matplotlib之pyplot模块坐标轴范围设置(autoscale(),xlim(),ylim())
这篇文章主要介绍了matplotlib之pyplot模块坐标轴范围设置(autoscale(),xlim(),ylim()),文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要的朋友们下面随着小编来一起学习学习吧2021-03-03
Python 中 Selenium 的 getAttribute()
本文将解释如何使用Selenium的getAttribute()方法,getAttribute() 方法可以检索元素属性,例如锚标记的 href 属性, 该函数最初将尝试返回指定属性的值,感兴趣的朋友跟随小编一起看看吧2023-11-11












最新评论