用Python实现流星雨效果的方法详解
更新时间:2021年12月20日 15:08:24 作者:微小冷
这篇文章主要为大家介绍了Python实现流星雨效果的方法,具有一定的参考价值,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下,希望能够给你带来帮助<BR>
流星雨的前提是得先有一个流星,所谓流星,就是一个拖着尾巴的直线。所谓拖着尾巴,实际上是我们的浪漫想象,实质无非是尺寸和颜色的渐变罢了。
而matplotlib并不能给一条曲线映射多个颜色,故而可将一条线拆分成多条,效果如图所示
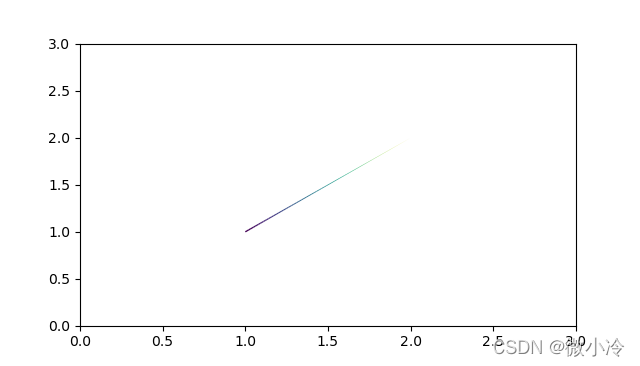
代码为
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection x0,y0 = 1,1 #此为流星位置 ts = np.arange(0,1,0.01) #参数 xs,ys = x0+ts, y0+ts #绘图线条 points = np.array([xs, ys]).T.reshape(-1, 1, 2) segments = np.concatenate([points[:-1], points[1:]], axis=1) ax = plt.subplot() lc = LineCollection(segments, cmap='viridis') lc.set_array(ts) lc.set_linewidth(ts[::-1]) line = ax.add_collection(lc) ax.set_xlim(0, 3) ax.set_ylim(0, 3) plt.show()
接下来就要把这个流星变成流星雨,很简单,多加一些流星就可以了,效果如下,尽管是在白天,但是不是感觉有点意思了。
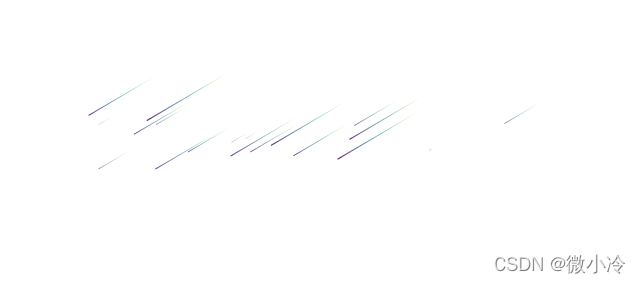
代码为
from numpy.random import rand, randint
N,L = 20,100 #流星个数和线段数
ts = np.array([
np.linspace(0,rand(),L) for _ in range(N)]).T
x0,y0 = rand(2*N).reshape(2,1,N)
x0 *= 5
xs,ys = x0+ts, y0+ts #绘图线条1
points = np.array([xs, ys]).T.reshape(N,L,-1,2)
ax = plt.subplot()
for i in range(N):
segs = np.concatenate([points[i][:-1], points[i][1:]], axis=1)
lc = LineCollection(segs, cmap='viridis')
lc.set_array(ts[:,i])
lc.set_linewidth(ts[::-1,i])
ax.add_collection(lc)
ax.set_xlim(0, 6)
ax.set_ylim(-2, 3)
ax.set_axis_off() #取消坐标轴
plt.show()
如果想让天黑下去,方法为
plt.figure(facecolor="black") #将背景设为黑色
此外,背景设为黑色之后,注意要把颜色映射调整一下,想知道更多具体的颜色映射表戳这里:matplotlib中的伪彩映射
lc = LineCollection(segs, cmap='viridis_r')
所以就是这种
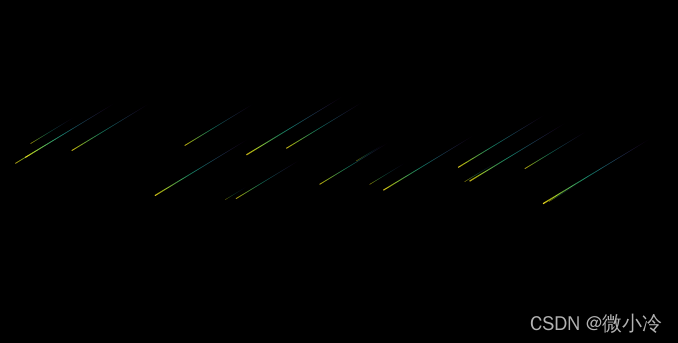
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注脚本之家的更多内容!
相关文章

python manage.py createsuperuser运行错误问题解决
这篇文章主要介绍了python manage.py createsuperuser运行错误,本文给大家分享错误复现及解决方案,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧2023-10-10
可用于监控 mysql Master Slave 状态的python代码
用于监控MySQL Master Slave 状态的python代码,有需要的朋友可以参考下2013-02-02












最新评论