python中的elasticsearch_dsl查询语句转换成es查询语句详解
更新时间:2023年07月25日 09:50:39 作者:IT之一小佬
这篇文章主要介绍了python中的elasticsearch_dsl查询语句转换成es查询语句详解,ElasticSearch在实际生产里通常和LogStash,Kibana,FileBeat一起构成Elastic Stack来使用,它是这些组件里面最核心的一个,需要的朋友可以参考下
elasticsearch_dsl查询语句转换成es语句
使用代码运行效果来演示转换结果。
示例代码1:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.104.49:9200"], timeout=20) # print(es) res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query().query() # 当调用.query()方法多次时,内部会使用&操作符 print(res.to_dict())
运行结果:

示例代码2:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = ~Q("match", title="python")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:
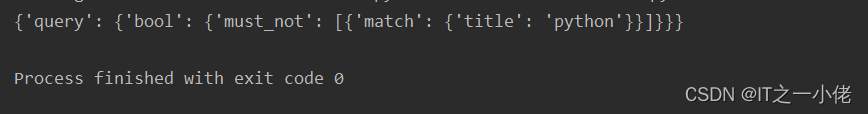
示例代码3:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q('match', name='张') & Q("match", name="北")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:
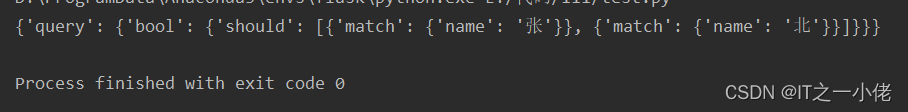
示例代码4:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("bool", must=[Q("match", address="山")], should=[Q("match", gender="男"), Q("match", emplyer="AAA")], minimum_should_match=1)
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:

示例代码5: 【分页】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("bool", must=[Q("match", address="山")], should=[Q("match", gender="男"), Q("match", emplyer="AAA")], minimum_should_match=1)
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)[2: 5]
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:

示例代码6: 【聚合】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("match", sex='男')
a = A("terms", field="gender")
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
res.aggs.bucket("gender_terms", a)
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:

示例代码7: 【聚合】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("match", sex='男')
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
res.aggs.bucket("per_gender", "terms", field="gender")
res.aggs["per_gender"].metric("sum_age", "sum", field="age")
res.aggs["per_gender"].bucket("terms_balance", "terms", field="balance")
res.aggs["per_gender"].bucket("terms_balance2", "terms", field="balance2")
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:


示例代码8: 【聚合内置排序】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("match", sex='男')
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
res.aggs.bucket("agg_age", "terms", field="age", order={"_count": "desc"})
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:


示例代码9:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("match", sex='男')
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q)
res.aggs.bucket("agg_age", "terms", field="age", order={"_count": "asc"}).metric("avg_age", "avg", field="age")
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:


示例代码10: 【_source字段】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
q = Q("match", sex='男')
res = Search(using=es, index="test_index").query(q).source(['account_number', 'address'])
print(res.to_dict())运行结果:
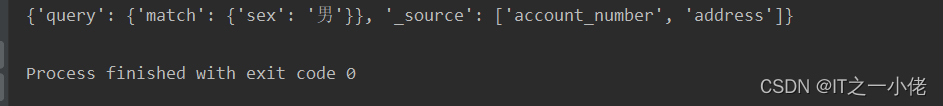
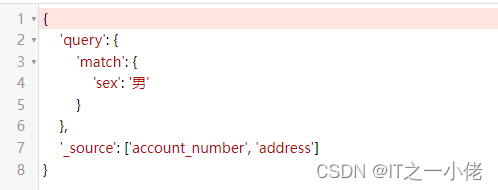
示例代码11:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
# 方式一:
# 省份为北京
q1 = Q("match", province="北京")
# 25或30岁的男性信息
q2 = Q("bool", must=[Q("terms", age=[25, 30]), Q("term", gender="男")])
# and
q = q1 & q2
res = s.query(q)
print(res.to_dict())
# for data in res:
# print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())
print("*" * 100)
# 方式二
# 省份为北京
q1 = Q("match", province="北京")
# 25或30岁的信息
# q2 = Q("bool", must=[Q("terms", age=[25, 30]), Q("term", gender="男")])
q2 = Q("term", age=25) | Q("term", age=30)
# 男性
q3 = Q("term", gender="男")
res = s.query(q1).query(q2).query(q3) # 多次query就是& ==> and 操作
print(res.to_dict())
# for data in res:
# print(data.to_dict())
print("共查到%d条数据" % res.count())运行结果:



示例代码12:
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
s.query()
q = A("terms", field="age", size=100).metric("age_per_balance", "avg", field="balance")
s.aggs.bucket("res", q)
print(s.to_dict())运行结果:

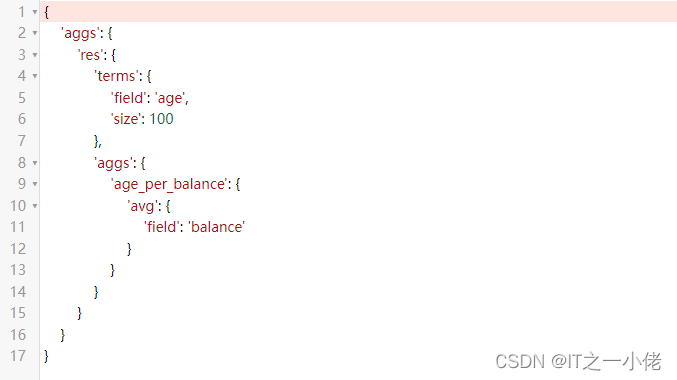
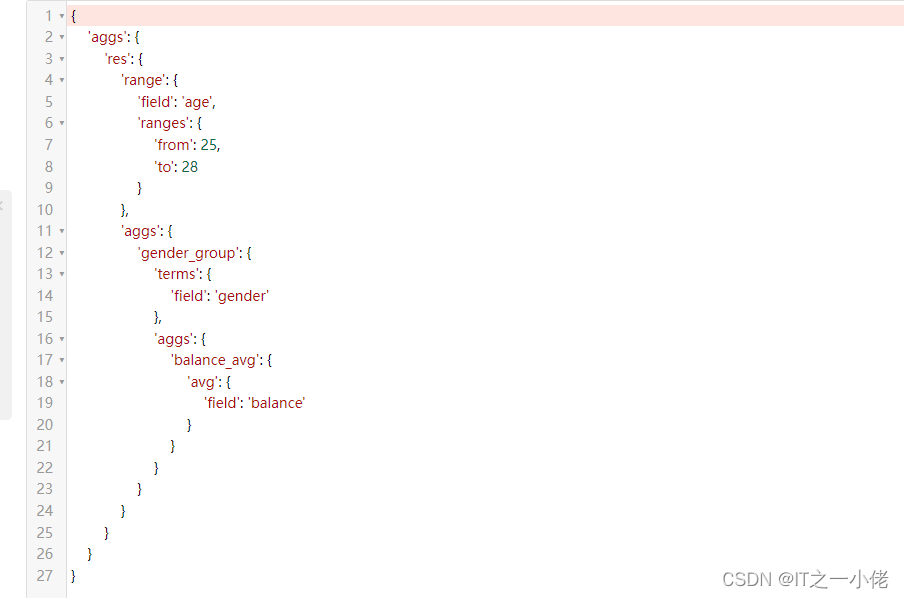
示例代码13: 【多次嵌套聚合】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
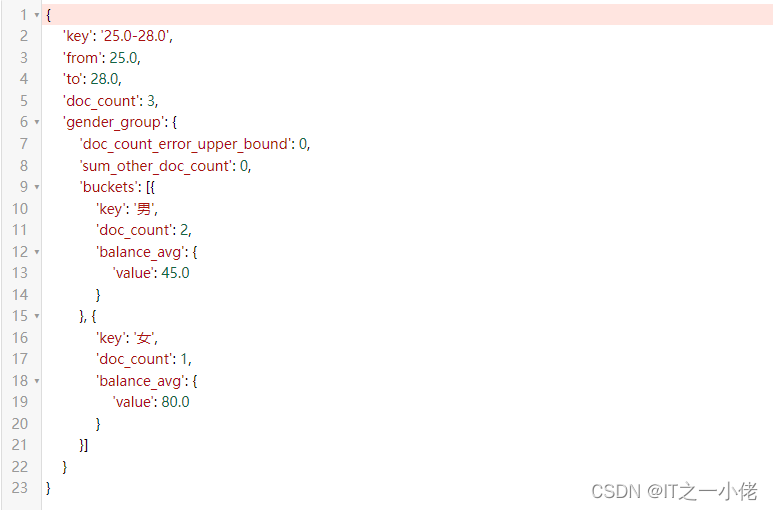
a1 = A("range", field="age", ranges={"from": 25, "to": 28})
a2 = A("terms", field="gender")
a3 = A("avg", field="balance")
s.aggs.bucket("res", a1).bucket("gender_group", a2).metric("balance_avg", a3)
print(s.to_dict())运行结果:


示例代码14: 【使用pycharm打断点查看查询语句】
from elasticsearch_dsl import connections, Search, Q, A
# 连接es
es = connections.create_connection(hosts=["192.168.124.49:9200"], timeout=20)
# print(es)
s = Search(using=es, index="account_info")
a1 = A("range", field="age", ranges={"from": 25, "to": 28})
a2 = A("terms", field="gender")
a3 = A("avg", field="balance")
s.aggs.bucket("res", a1).bucket("gender_group", a2).metric("balance_avg", a3)
# print(s.to_dict())
# 执行并拿到返回值
response = s.execute()
# res是bucket指定的名字
for data in response.aggregations.res:
print(data.to_dict())运行结果:

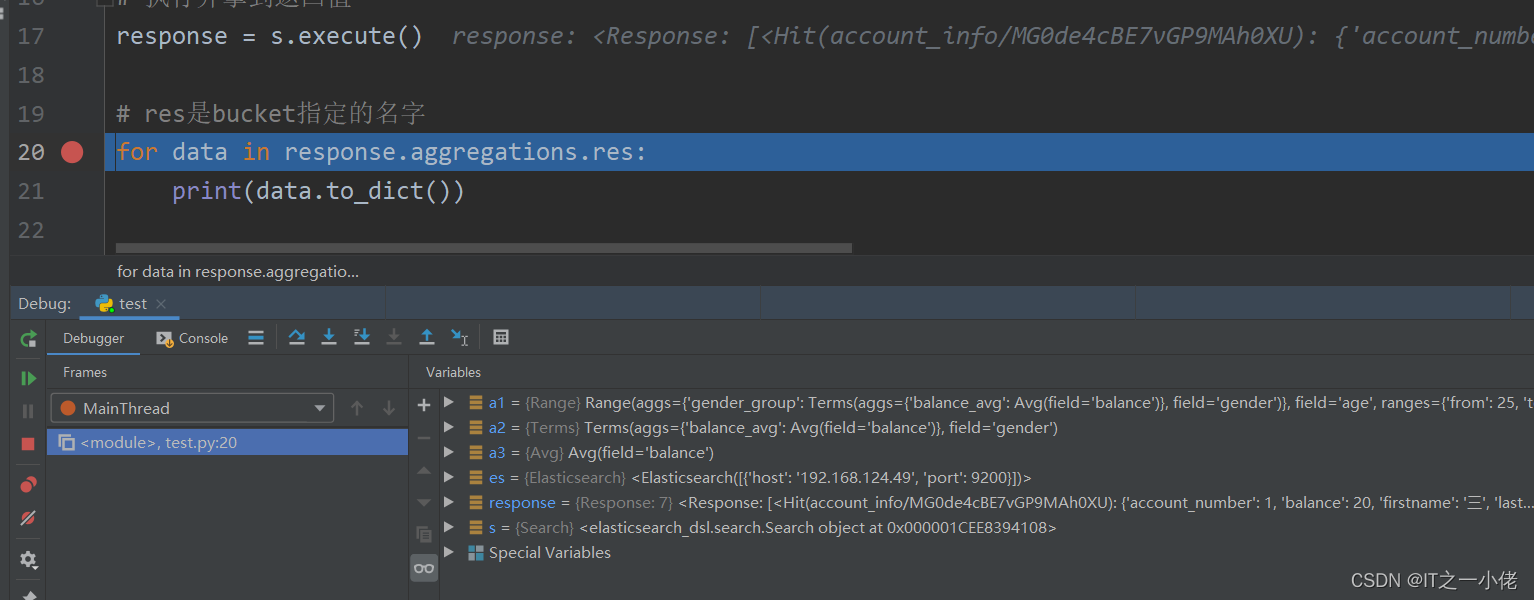

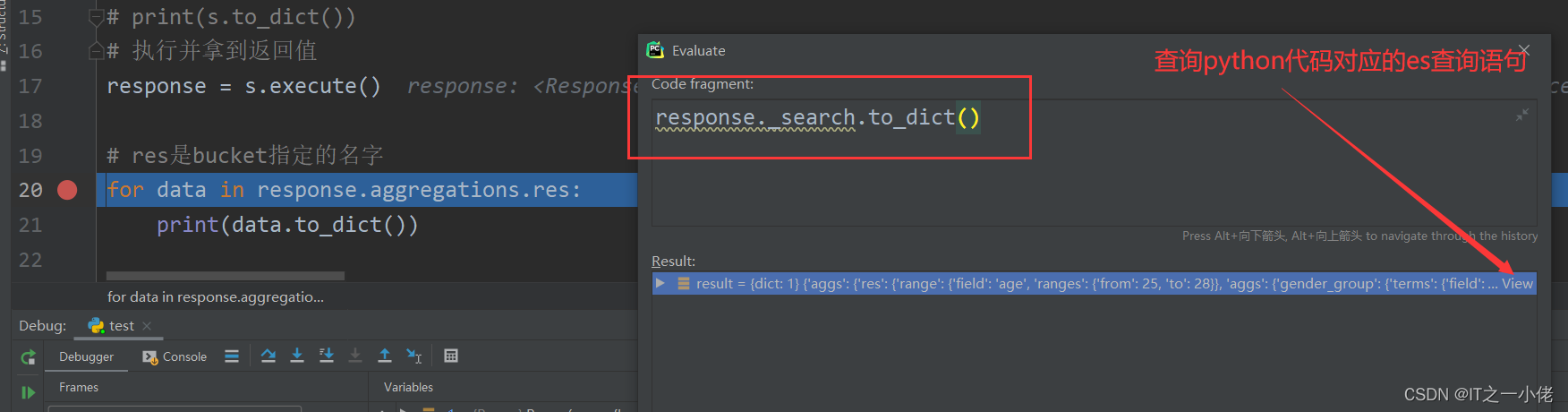

注意:即使数据库中没有数据,也可以打印出查询语句!
到此这篇关于python中的elasticsearch_dsl查询语句转换成es查询语句详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python的elasticsearch_dsl转换es内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!
相关文章

Jupyter Notebook内使用argparse报错的解决方案
这篇文章主要介绍了在Jupyter Notebook内使用argparse报错的解决方案,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教2021-06-06
Python批量处理PDF图片的操作指南(插入、压缩、提取、替换、分页、旋转、删除)
图片是 PDF 文档的核心元素之一,它们不仅能够增强文档的视觉吸引力,还能有效传达信息,帮助读者更好地理解内容和主题,在实际操作中,我们常需要对PDF中的图片进行多种处理,这篇文章将详细介绍如何使用Python在PDF中实现图片插入、提取、替换、压缩等操作2025-04-04












最新评论