基于Python schedule的任务调度详解
schedule 是Python的第三方任务调度库,可以用来做定时任务,API简单易用,可以按照秒,分,小时,日期或者自定义事件执行时间,不需要额外的流程,非常轻量级,没有外部依赖,兼容Python 3.7、3.8、3.9、3.10和3.11。
安装
$ pip install schedule
每隔一段时间执行一次
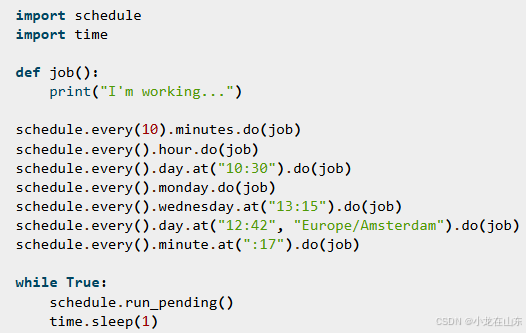
import schedule
import time
def job():
print("I'm working...")
# Run job every 3 second/minute/hour/day/week,
# Starting 3 second/minute/hour/day/week from now
schedule.every(3).seconds.do(job)
schedule.every(3).minutes.do(job)
schedule.every(3).hours.do(job)
schedule.every(3).days.do(job)
schedule.every(3).weeks.do(job)
# Run job every minute at the 23rd second
schedule.every().minute.at(":23").do(job)
# Run job every hour at the 42nd minute
schedule.every().hour.at(":42").do(job)
# Run jobs every 5th hour, 20 minutes and 30 seconds in.
# If current time is 02:00, first execution is at 06:20:30
schedule.every(5).hours.at("20:30").do(job)
# Run job every day at specific HH:MM and next HH:MM:SS
schedule.every().day.at("10:30").do(job)
schedule.every().day.at("10:30:42").do(job)
schedule.every().day.at("12:42", "Europe/Amsterdam").do(job)
# Run job on a specific day of the week
schedule.every().monday.do(job)
schedule.every().wednesday.at("13:15").do(job)
schedule.every().minute.at(":17").do(job)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
用装饰器执行
用@repeat装饰器来设置执行参数。
from schedule import every, repeat, run_pending
import time
@repeat(every(10).minutes)
def job():
print("I am a scheduled job")
while True:
run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
给任务传递参数
do()可以传递额外的参数给任务。
import schedule
def greet(name):
print('Hello', name)
schedule.every(2).seconds.do(greet, name='Alice')
schedule.every(4).seconds.do(greet, name='Bob')
from schedule import every, repeat
@repeat(every().second, "World")
@repeat(every().day, "Mars")
def hello(planet):
print("Hello", planet)
取消任务
import schedule
def some_task():
print('Hello world')
job = schedule.every().day.at('22:30').do(some_task)
schedule.cancel_job(job)
schedule.cancel_job(job)取消任务。
执行一次任务
启动任务后,调用schedule.CancelJob取消任务,就只执行一次任务。
import schedule
import time
def job_that_executes_once():
# Do some work that only needs to happen once...
return schedule.CancelJob
schedule.every().day.at('22:30').do(job_that_executes_once)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
获取所有的任务
schedule.get_jobs()获取所有任务。
import schedule
def hello():
print('Hello world')
schedule.every().second.do(hello)
all_jobs = schedule.get_jobs()
取消所有任务
schedule.clear()取消所有任务。
import schedule
def greet(name):
print('Hello {}'.format(name))
schedule.every().second.do(greet)
schedule.clear()
获取指定任务
通过tag设置标签,schedule.get_jobs('friend')来获取指定标签的任务。
import schedule
def greet(name):
print('Hello {}'.format(name))
schedule.every().day.do(greet, 'Andrea').tag('daily-tasks', 'friend')
schedule.every().hour.do(greet, 'John').tag('hourly-tasks', 'friend')
schedule.every().hour.do(greet, 'Monica').tag('hourly-tasks', 'customer')
schedule.every().day.do(greet, 'Derek').tag('daily-tasks', 'guest')
friends = schedule.get_jobs('friend')
取消指定任务
import schedule
def greet(name):
print('Hello {}'.format(name))
schedule.every().day.do(greet, 'Andrea').tag('daily-tasks', 'friend')
schedule.every().hour.do(greet, 'John').tag('hourly-tasks', 'friend')
schedule.every().hour.do(greet, 'Monica').tag('hourly-tasks', 'customer')
schedule.every().day.do(greet, 'Derek').tag('daily-tasks', 'guest')
schedule.clear('daily-tasks')
指定区间运行任务
def my_job():
print('Foo')
# Run every 5 to 10 seconds.
schedule.every(5).to(10).seconds.do(my_job)
执行任务直到指定时间(超时)
import schedule
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, time
def job():
print('Boo')
# run job until a 18:30 today
schedule.every(1).hours.until("18:30").do(job)
# run job until a 2030-01-01 18:33 today
schedule.every(1).hours.until("2030-01-01 18:33").do(job)
# Schedule a job to run for the next 8 hours
schedule.every(1).hours.until(timedelta(hours=8)).do(job)
# Run my_job until today 11:33:42
schedule.every(1).hours.until(time(11, 33, 42)).do(job)
# run job until a specific datetime
schedule.every(1).hours.until(datetime(2020, 5, 17, 11, 36, 20)).do(job)
执行到下一个任务
schedule.idle_seconds()用来获取下一个任务计划执行的秒数。如果没有任务了,返回None。
import schedule
import time
def job():
print('Hello')
schedule.every(5).seconds.do(job)
while 1:
n = schedule.idle_seconds()
if n is None:
# no more jobs
break
elif n > 0:
# sleep exactly the right amount of time
time.sleep(n)
schedule.run_pending()
立即运行
import schedule
def job_1():
print('Foo')
def job_2():
print('Bar')
schedule.every().monday.at("12:40").do(job_1)
schedule.every().tuesday.at("16:40").do(job_2)
schedule.run_all()
# Add the delay_seconds argument to run the jobs with a number
# of seconds delay in between.
schedule.run_all(delay_seconds=10)
schedule.run_all()会让任务忽略计划,立即执行。schedule.run_all(delay_seconds=10)让任务恢复执行。
后台执行
import threading
import time
import schedule
def run_continuously(interval=1):
"""Continuously run, while executing pending jobs at each
elapsed time interval.
@return cease_continuous_run: threading. Event which can
be set to cease continuous run. Please note that it is
*intended behavior that run_continuously() does not run
missed jobs*. For example, if you've registered a job that
should run every minute and you set a continuous run
interval of one hour then your job won't be run 60 times
at each interval but only once.
"""
cease_continuous_run = threading.Event()
class ScheduleThread(threading.Thread):
@classmethod
def run(cls):
while not cease_continuous_run.is_set():
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(interval)
continuous_thread = ScheduleThread()
continuous_thread.start()
return cease_continuous_run
def background_job():
print('Hello from the background thread')
schedule.every().second.do(background_job)
# Start the background thread
stop_run_continuously = run_continuously()
# Do some other things...
time.sleep(10)
# Stop the background thread
stop_run_continuously.set()
并行执行
import threading
import time
import schedule
def job():
print("I'm running on thread %s" % threading.current_thread())
def run_threaded(job_func):
job_thread = threading.Thread(target=job_func)
job_thread.start()
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(run_threaded, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(run_threaded, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(run_threaded, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(run_threaded, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(run_threaded, job)
while 1:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
这里每个任务都启动一个线程来并行执行。
import time
import threading
import schedule
import queue
def job():
print("I'm working")
def worker_main():
while 1:
job_func = jobqueue.get()
job_func()
jobqueue.task_done()
jobqueue = queue.Queue()
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(jobqueue.put, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(jobqueue.put, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(jobqueue.put, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(jobqueue.put, job)
schedule.every(10).seconds.do(jobqueue.put, job)
worker_thread = threading.Thread(target=worker_main)
worker_thread.start()
while 1:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
这里用到用了一个任务队列来严格执行线程数。
设置时区
# Pass a timezone as a string
schedule.every().day.at("12:42", "Europe/Amsterdam").do(job)
# Pass an pytz timezone object
from pytz import timezone
schedule.every().friday.at("12:42", timezone("Africa/Lagos")).do(job)
以上就是基于Python schedule的任务调度详解的详细内容,更多关于Python schedule任务调度的资料请关注脚本之家其它相关文章!
相关文章

运行python提示no module named sklearn的解决方法
这篇文章主要介绍了运行python提示no module named sklearn的解决方法,需要的朋友可以参考下2020-11-11












最新评论