Java 小游戏开发之俄罗斯方块
更新时间:2017年07月22日 10:13:35 投稿:lqh
这篇文章主要介绍了Java 小游戏开发之俄罗斯方块的相关资料,这里实现俄罗斯方块的实例和实现效果给大家看下,学习java基础的朋友的好资料,需要的朋友可以参考下
Java项目 俄罗斯方块
一、心得
二、游戏实例
游戏截图
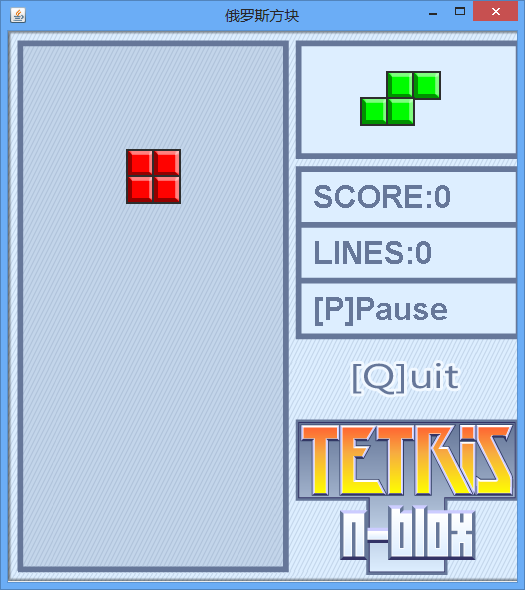
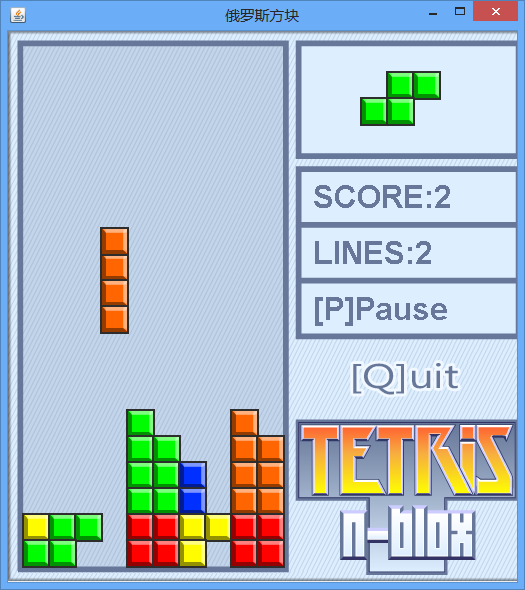
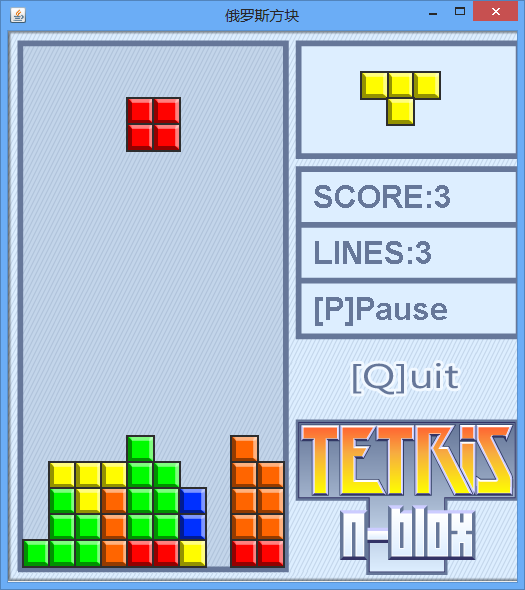
目录结构
三、代码
1、主界面 Tetris.java
package com.fry.tetris;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 4格方块
*/
public class Tetromino {
protected Cell[] cells = new Cell[4];
/** 保存旋转的相对于轴位置状态 */
protected State[] states;
/** 随机生成 4格方块, 使用简单工厂方法模式!
* randomTetromino 随机生成一个四格方块
* 这个方面的返回值是多态的!
* */
public static Tetromino randomTetromino(){
Random r = new Random();
int type = r.nextInt(7);
switch(type){
case 0: return new T();
case 1: return new I();
case 2: return new J();
case 3: return new L();
case 4: return new O();
case 5: return new S();
case 6: return new Z();
}
return null;
}
public Cell[] getCells() {
return cells;
}
/** 下落 */
public void softDrop(){
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
cells[i].moveDown();
}
}
public void moveRight(){
//System.out.println("moveRight()");
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
this.cells[i].moveRight();
}
}
public void moveLeft(){
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
cells[i].moveLeft();
}
}
private int index = 100000;
/** 在 Tetromino 上添加方法 */
public void rotateRight() {
index++;//index = 10001
// index % states.length = 10001 % 4 = 1
State s = states[index%states.length];//s1
// [0] + s1 = [1]
Cell o = cells[0];//获取当前的轴
//轴与相对位置的和作为旋转以后的格子位置
cells[1].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row1);
cells[1].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col1);
cells[2].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row2);
cells[2].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col2);
cells[3].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row3);
cells[3].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col3);
}
/** 在 Tetromino 上添加方法 */
public void rotateLeft() {
index--;//index = 10001
// index % states.length = 10001 % 4 = 1
State s = states[index%states.length];//s1
// [0] + s1 = [1]
Cell o = cells[0];//获取当前的轴
cells[1].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row1);
cells[1].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col1);
cells[2].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row2);
cells[2].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col2);
cells[3].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row3);
cells[3].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col3);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Arrays.toString(cells);
}
/** Tetromino 类中添加的 内部类 用于记录旋转状态 */
protected class State{
int row0,col0,row1,col1,row2,col2,row3,col3;
public State(int row0, int col0, int row1, int col1,
int row2, int col2,
int row3, int col3) {
this.row0 = row0;
this.col0 = col0;
this.row1 = row1;
this.col1 = col1;
this.row2 = row2;
this.col2 = col2;
this.row3 = row3;
this.col3 = col3;
}
}
}//Tetromino 类的结束
class T extends Tetromino{
public T() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.T);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.T);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.T);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.T);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1, 0),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, 0,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,0),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, 0,1)};
}
}
class I extends Tetromino{
public I() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.I);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.I);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.I);
cells[3] = new Cell(0, 6, Tetris.I);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, 0,-2),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0,2,0)};
}
}
class L extends Tetromino {
public L() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.L);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.L);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.L);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 3, Tetris.L);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1,-1 ),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, -1,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,1),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, 1,1)};
}
}
class J extends Tetromino {
public J() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.J);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.J);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.J);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.J);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1,1),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, 1,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,-1),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, -1,1 )};
}
}
class S extends Tetromino {
public S() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.S);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.S);
cells[2] = new Cell(1, 3, Tetris.S);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.S);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,-1, 1,0 ),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,1, 0,1 )};
}
}
class Z extends Tetromino {
public Z() {
cells[0] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.Z);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.Z);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.Z);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.Z);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, -1,-1, -1,0, 0,1 ),
new State(0,0, -1,1, 0,1, 1,0 )};
}
}
class O extends Tetromino {
public O() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.O);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.O);
cells[2] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.O);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.O);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,0, 1,1 ),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,0, 1,1 )};
}
}
二、Cell.java
package com.fry.tetris;
import java.awt.Image;
/**
* 格子
* 每一个小格子,就有所在的行 列 和图片
*/
public class Cell {
private int row;
private int col;
//private int color;
private Image image;//格子的贴图
public Cell() {
}
public Cell(int row, int col, Image image) {
super();
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.image = image;
}
public int getRow() {
return row;
}
public void setRow(int row) {
this.row = row;
}
public int getCol() {
return col;
}
public void setCol(int col) {
this.col = col;
}
public Image getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(Image image) {
this.image = image;
}
public void moveRight(){
col++;
//System.out.println("Cell moveRight()" + col);
}
public void moveLeft(){
col--;
}
public void moveDown(){
row++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "["+row+","+col+"]";
}
}
三、功能实现 Tetromino.java
package com.fry.tetris;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 4格方块
*/
public class Tetromino {
protected Cell[] cells = new Cell[4];
/** 保存旋转的相对于轴位置状态 */
protected State[] states;
/** 随机生成 4格方块, 使用简单工厂方法模式!
* randomTetromino 随机生成一个四格方块
* 这个方面的返回值是多态的!
* */
public static Tetromino randomTetromino(){
Random r = new Random();
int type = r.nextInt(7);
switch(type){
case 0: return new T();
case 1: return new I();
case 2: return new J();
case 3: return new L();
case 4: return new O();
case 5: return new S();
case 6: return new Z();
}
return null;
}
public Cell[] getCells() {
return cells;
}
/** 下落 */
public void softDrop(){
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
cells[i].moveDown();
}
}
public void moveRight(){
//System.out.println("moveRight()");
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
this.cells[i].moveRight();
}
}
public void moveLeft(){
for(int i=0; i<cells.length; i++){
cells[i].moveLeft();
}
}
private int index = 100000;
/** 在 Tetromino 上添加方法 */
public void rotateRight() {
index++;//index = 10001
// index % states.length = 10001 % 4 = 1
State s = states[index%states.length];//s1
// [0] + s1 = [1]
Cell o = cells[0];//获取当前的轴
//轴与相对位置的和作为旋转以后的格子位置
cells[1].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row1);
cells[1].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col1);
cells[2].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row2);
cells[2].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col2);
cells[3].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row3);
cells[3].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col3);
}
/** 在 Tetromino 上添加方法 */
public void rotateLeft() {
index--;//index = 10001
// index % states.length = 10001 % 4 = 1
State s = states[index%states.length];//s1
// [0] + s1 = [1]
Cell o = cells[0];//获取当前的轴
cells[1].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row1);
cells[1].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col1);
cells[2].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row2);
cells[2].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col2);
cells[3].setRow(o.getRow()+s.row3);
cells[3].setCol(o.getCol()+s.col3);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Arrays.toString(cells);
}
/** Tetromino 类中添加的 内部类 用于记录旋转状态 */
protected class State{
int row0,col0,row1,col1,row2,col2,row3,col3;
public State(int row0, int col0, int row1, int col1,
int row2, int col2,
int row3, int col3) {
this.row0 = row0;
this.col0 = col0;
this.row1 = row1;
this.col1 = col1;
this.row2 = row2;
this.col2 = col2;
this.row3 = row3;
this.col3 = col3;
}
}
}//Tetromino 类的结束
class T extends Tetromino{
public T() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.T);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.T);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.T);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.T);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1, 0),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, 0,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,0),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, 0,1)};
}
}
class I extends Tetromino{
public I() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.I);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.I);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.I);
cells[3] = new Cell(0, 6, Tetris.I);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, 0,-2),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0,2,0)};
}
}
class L extends Tetromino {
public L() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.L);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.L);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.L);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 3, Tetris.L);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1,-1 ),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, -1,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,1),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, 1,1)};
}
}
class J extends Tetromino {
public J() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.J);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.J);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.J);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.J);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,-1, 0,1, 1,1),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,0, 1,-1),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 0,-1, -1,-1),
new State(0,0, 1,0, -1,0, -1,1 )};
}
}
class S extends Tetromino {
public S() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.S);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.S);
cells[2] = new Cell(1, 3, Tetris.S);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.S);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,-1, 1,0 ),
new State(0,0, -1,0, 1,1, 0,1 )};
}
}
class Z extends Tetromino {
public Z() {
cells[0] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.Z);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 3, Tetris.Z);
cells[2] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.Z);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.Z);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, -1,-1, -1,0, 0,1 ),
new State(0,0, -1,1, 0,1, 1,0 )};
}
}
class O extends Tetromino {
public O() {
cells[0] = new Cell(0, 4, Tetris.O);
cells[1] = new Cell(0, 5, Tetris.O);
cells[2] = new Cell(1, 4, Tetris.O);
cells[3] = new Cell(1, 5, Tetris.O);
states = new State[]{
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,0, 1,1 ),
new State(0,0, 0,1, 1,0, 1,1 )};
}
}
以上就是java实现俄罗斯方块的实例,如有疑问请留言或者到本站社区讨论,感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!
相关文章

阿里的Easyexcel读取Excel文件的方法(最新版本)
这篇文章主要介绍了阿里的Easyexcel读取Excel文件(最新版本)的方法,本文通过示例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2022-12-12
网关Spring Cloud Gateway HTTP超时配置问题
这篇文章主要介绍了网关Spring Cloud Gateway HTTP超时配置问题,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助,如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教2024-01-01
spring boot常见get 、post请求参数处理、参数注解校验、参数自定义注解校验问题解析
这篇文章主要介绍了spring boot常见get 、post请求参数处理、参数注解校验、参数自定义注解校验,本文通过示例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下2023-09-09












最新评论