深入理解 line-height 和 vertical-align
几个概念
- line box:包裹 inline box 的一个盒子,一个或多个 line box 堆叠撑起一个 HTML 元素。
- inline(-level) box:可以是一个由行内元素包裹的盒子,也可以是一个纯文字的匿名盒子。
- content area:对于非替换元素来说,content area 的范围由 font-size 以及字体本身决定;对于替换元素来说,由元素自有宽高决定。
- baseline:一个元素基线的位置由该元素内字母 x 底部所在的位置决定,当然字体不同基线所在的位置也就不同。
通过一段代码可以理解一下:
div {
background-color: #ccc;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fff;
}
span {
color: red;
}
<div>文字1<span>文字2</span>文字3</div>

白色的文字就是一个匿名 inline box,红色的文字是一个由 span 包裹的 inline box。这三个 inline box 组成一个 line box,可以理解为灰色的区域,因为在这个例子里就是由一个 line box 撑开了 div。如果有多行的文字,那就有多个 line box。
关于 content area,W3C 有一段这样的解释:
CSS 2.1 does not define what the content area of an inline box is (see 10.6.1 above) and thus different UAs may draw the backgrounds and borders in different places.
这篇文章对非替换元素 content area 的定义就是自有宽高加上 margin,padding 以及 border。我认为应该将 content area 理解为 content box。
line box 高度
浏览器会计算 line box 中每一个 inline box 的高度,对于不同的 inline box 计算方式有所不同:
如果是一个替换元素(比如 img,input),inline-* 元素或者是 flexbox 中的子元素,高度由其 margin box 决定;
inline-block 元素:
div {
background-color: #ccc;
color: #fff;
}
span {
display: inline-block;
height: 30px;
margin: 10px;
background: #fff;
color: red;
}
<div>xxx<span>xxx</span>xxx</div>
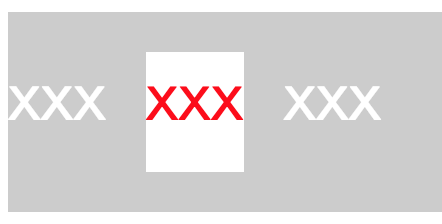
这里 span inline box 的高度就是 height + margin 2。如果 height 的值是 auto,高度就是等于 line-height + margin 2。
如果是一个非替换元素,高度由它的 line-height 决定,而不是 content area,虽然有时候看起来像 content area 撑开了 line box 的高度。
div {
background-color: #ccc;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fff;
font-family: Sana;
}
span {
background: #fff;
color: red;
}
<div>xxx<span>xxx</span>xxx</div>
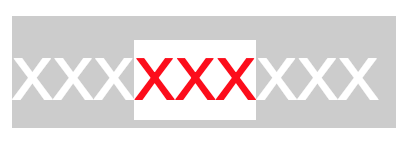
这张图片可以明显地看出撑开 line box 的是 line-height,而不是 content area。
这篇文章用了 virtual-area height 来表示 line-height 撑开的高度,而我的理解其实就是 inline box 的高度。
line box 中所有 inline box 的最高点以及最低点决定了它的高度(该计算包括了 strut 的高度,后文会提到 strut)。
非替换元素的的 margin,padding 以及 border 并不会影响 line box 高度的计算。当一个 inline-level box 的 line-height 小于 content area 的时候,line box 的高度就会小于 content area,此时元素的 background 以及 padding 等就会溢出到 line box 之外。
以下代码可以说明这个问题:
div {
background: #eee;
border: 1px solid #000;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 50px;
line-height: 10px;
}
span {
background: red;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
}
<div><span>xxx</span></div>

leading:
content area 的高度与 inline box 的高度差就是 leading,这个 leading 会等分被添加到 content area 的顶部与底部,所以说 content area 永远位于 inline box 的中间(垂直居中)。
strut:
浏览器认为每一个 line box 的起始位置都存在一个宽度为 0,没有任何字符的 匿名 inline box,称为 strut,这个 strut 是会从父元素继承 line-height 的,因此它的高度会影响整个 line box 高度的计算。
一个例子

div { background: #eee; border: 1px solid #000; box-sizing: border-box; }
<div><img src="./image.png" alt=""></div>
在图片中可以看到 img 与外层的 div 存在一个间隙,这就是上文提到的 strut 造成的。
在这个例子中,默认情况下 img 的底边与父元素的基线对齐(img { vertical-align: baseline }),而这个基线实际上就是 strut 基线所在的位置。如下图所示:

strut 其实就相当于一个不可见的字母 x,上文已经提到 strut 本身是具有 line-height 的,所以就导致图片底部多了一段间隙。
总结一下存在间隙原因:
- strut 存在 line-height
- vertical-align 默认值为 baseline
对应的解决方案:
- 修改 strut 的 line-height,因为 strut 的 line-height 不是能够直接设置的,所以需要设置父元素的 line-height,然后让 strut 继承,或者修改 font-size
- 将 vertical-align 设置为其他值line-height
W3C 中对于 line-height 的解释是这样的:
On a block container element whose content is composed of inline-level elements, 'line-height' specifies the minimal height of line boxes within the element. The minimum height consists of a minimum height above the baseline and a minimum depth below it, exactly as if each line box starts with a zero-width inline box with the element's font and line height properties. We call that imaginary box a "strut."
我的简单理解是,对于由行内元素组成的块级元素而言,line-height 决定了 line box 的最小高度,浏览器会假定每一个 line box 以一个宽度为 0 的 inline box (strut)开始,而这个 strut 从父元素继承到 font 以及 line-height。
- normal 是 line-height 的默认值,W3C 对它并没有一个明确的定义。normal 会将 content area 作为一个计算因素。
- line-height 并不是两条 baseline 之间的距离。
line-height的值推荐使用数值,而不是使用 em 单位,因为 em 单位会根据从父元素继承到的font-size来计算行高。
vertical-align
W3C 对 baseline 以及 middle 的定义如下:
baseline: Align the baseline of the box with the baseline of the parent box. If the box does not have a baseline, align the bottom margin edge with the parent's baseline.
元素基线与父元素基线对齐,如果元素没有基线,比如 img,则使用 margin 底边与父元素基线对齐。
middle: Align the vertical midpoint of the box with the baseline of the parent box plus half the x-height of the parent.
元素的垂直中点位置与父元素的基线加上一半 x-height 的位置对齐。
参考
Deep dive CSS: font metrics, line-height and vertical-align
https://meyerweb.com/eric/css/inline-format.html
https://www.zhangxinxu.com/wordpress/2015/08/css-deep-understand-vertical-align-and-line-height/
https://www.w3.org/TR/CSS2/visudet.html#inline-box-height
相关文章
- CSS Grid 是一种二维布局系统,可以同时控制行和列,相比 Flex(一维布局),更适合用在整体页面布局或复杂模块结构中,这篇文章主要介绍了前端CSS Grid 布局详解,需要的朋2025-04-16
- CSS 中的 padding 和 margin 是两个非常基础且重要的属性,它们用于控制元素周围的空白区域,本文将详细介绍 padding 和 margin 的概念、区别以及如何在实际项目中使用它们2025-04-07
- will-change 是一个 CSS 属性,用于告诉浏览器某个元素在未来可能会发生哪些变化,本文给大家介绍CSS will-change 属性详解,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧2025-04-07
- 本文给大家分享在 CSS 中,去除a标签(超链接)的下划线的几种方法,本文给大家介绍的非常详细,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧2025-04-07
 在前端开发中,CSS(层叠样式表)不仅是用来控制网页的外观和布局,更是实现复杂交互和动态效果的关键技术之一,随着前端技术的不断发展,CSS的用法也日益丰富和高级,本文将2025-04-07
在前端开发中,CSS(层叠样式表)不仅是用来控制网页的外观和布局,更是实现复杂交互和动态效果的关键技术之一,随着前端技术的不断发展,CSS的用法也日益丰富和高级,本文将2025-04-07css中的 vertical-align与line-height作用详解
文章详细介绍了CSS中的`vertical-align`和`line-height`属性,包括它们的作用、适用元素、属性值、常见使用场景、常见问题及解决方案,感兴趣的朋友跟随小编一起看看吧2025-03-26浅析CSS 中z - index属性的作用及在什么情况下会失效
z-index属性用于控制元素的堆叠顺序,值越大,元素越显示在上层,它需要元素具有定位属性(如relative、absolute、fixed或sticky),本文给大家介绍CSS 中z - index属性的作用2025-03-21- 文章详细介绍了CSS中的打印媒体查询@mediaprint包括基本语法、常见使用场景和代码示例,如隐藏非必要元素、调整字体和颜色、处理链接的URL显示、分页控制、调整边距和背景等2025-03-18

CSS模拟 html 的 title 属性(鼠标悬浮显示提示文字效果)
本文介绍了如何使用CSS模拟HTML的title属性,通过鼠标悬浮显示提示文字效果,通过设置`.tipBox`和`.tipBox.tipContent`的样式,实现了提示内容的隐藏和显示,感兴趣的朋友一起2025-03-10
前端 CSS 动态设置样式::class、:style 等技巧(推荐)
本文介绍了Vue.js中动态绑定类名和内联样式的两种方法:对象语法和数组语法,通过对象语法,可以根据条件动态切换类名或样式;通过数组语法,可以同时绑定多个类名或样式,此外2025-02-26





最新评论