Java异步编程Future应用方式
1 Future接口介绍
此时有的人会说,对于任务并行需求,直接通过多线程实现不就可以了, 要注意,对于多线程的实现,java提供了三种方式:继承Thread类、实现Runnable接口和实现Callable接口。
但是业务代码在执行时会考虑执行顺序的问题,直接基于这些方式实现多线程会出现两个问题:
- 1)要想控制线程执行顺序,会通过join()等待线程结束,那这样的话又回归到了阻塞式调用的思路上,违背了并行的需求。 另外还可以通过wait()、notify()、notifyAll()结合状态变量实现,但实现起来过于复杂。
- 2)线程执行完之后,要想获取线程执行结果,还要用过共享变量或线程间通信等方式来获取,同样过于复杂。为了解决上述问题,Java5中推出了Future,其初衷就是用于构建复杂并行操作。内部方法在返回时,不是返回一个值,而是返回Future对象。其本质是在执行主业务的同时,异步的执行其他分业务,从而利用原本需要同步执行时的等待时间去执行其他的业务,当需要获取其结果时,再进行获取。
Java官网对于Future的描述:

Future表示异步计算的结果。 提供了一些方法来检查计算是否完成,等待其完成以及检索计算结果。 只有在计算完成后才可以使用get方法检索结果,必要时将其阻塞,直到准备就绪为止。 取消通过cancel方法执行。 提供了其他方法来确定任务是正常完成还是被取消。 一旦计算完成,就不能取消计算。
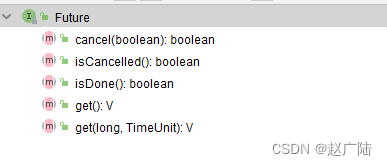
在Future接口中有五个抽象方法:
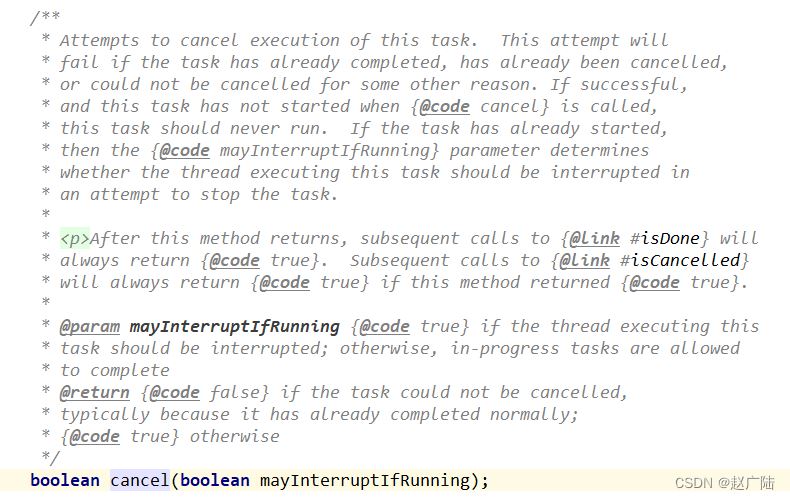
cancel():取消任务, 取消成功返回true;入参mayInterruptIfRunning表示是否允许取消正在执行中的任务。

isCancelled():返回布尔值,代表是否取消成功。

isDone():返回布尔值,代表是否执行完毕。
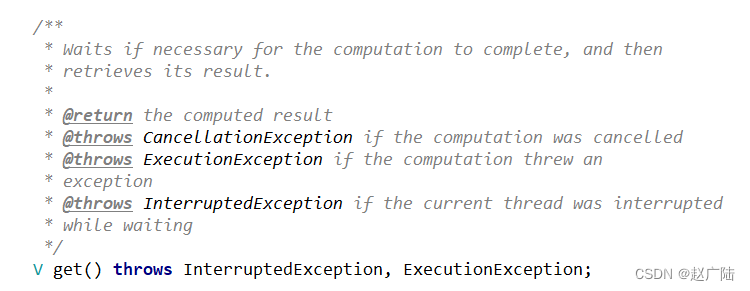
get():返回Future对象,获取执行结果,如果任务没有完成会阻塞到任务完成再返回。
2 Future应用
Future的使用通常需要配合ExecutorService和Callable一起
使用,使用示例如下:
public class FutureAsyncDemo {
static Random random = new Random();
static ExecutorService executor =
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//接收文章名称,获取并计算文章分数
public static int getArticleScore(String
aname){
Future<Integer> futureA =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreA());
Future<Integer> futureB =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreA());
Future<Integer> futureC =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreA());
doSomeThingElse();
Integer a = null;
try {
a = futureA.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer b = null;
try {
b = futureB.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer c = null;
try {
c = futureC.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
return a+b+c;
}
private static void doSomeThingElse() {
System.out.println("exec other
things");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getArticleScore("demo"))
;
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreA implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
//业务代码
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().g
etName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}执行结果
exec other things
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-3
pool-1-thread-2
159
上述方法改造了calculateArticleScore(),在其内部基于线程池调用重写了Callable接口中的call(),并在call()中对具体业务完成编码,并且让其在执行时睡三秒钟。根据结果可以看到,先调用了计算文章分数方法,其内部开启了子线程去执行任务,并且子线程在执行时,并没有阻塞主线程的执行。
当主线程需要结果时,在通过返回的Future来获取子任务中的返回值。
3 Future并行变串行问题解析
刚才已经基于Future演示了并行执行的效果,已经达到了期望,但是在使用的过程中,其实还有个坑需要说明。
对于Future的使用,如稍加不注意,就会让并行变为串行。
示例代码如下:
public class FutureAsyncDemo {
static ExecutorService executor =
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//接收文章名称,获取并计算文章分数
public static int getArticleScore(String
aname){
Future<Integer> futureA =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreA());
Future<Integer> futureB =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreB());
Future<Integer> futureC =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreC());
doSomeThingElse();
Integer a = 0;
try {
a = futureA.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer b = 0;
try {
b = futureB.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer c = 0;
try {
c = futureC.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
return a+b+c;
}
private static void doSomeThingElse() {
System.out.println("exec other
things");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getArticleScore("demo"))
;
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreA implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().g
etName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreB implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().g
etName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreC implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(30);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().g
etName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}上述代码加计算得分方法复制出来两份,各自休眠10秒、20秒、30秒。当方法返回Future之后,调用get()进行值获取时,发现每次调用时都需要进行等待。
这样可以发现,之前的并行现在变成了串行了!!!! 这个问题为什么会产生呢?需要看一下Future中对于get()的介绍
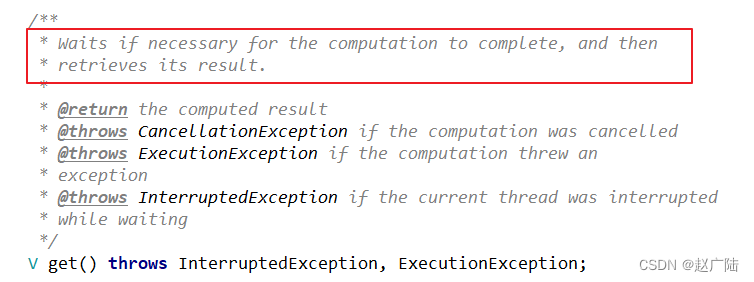
根据源码可知,当调用get()时,其会等待对应方法执行完毕后,才会返回结果,否则会一直等待。因为这个设定,所以上述代码则出现并行变串行的效果。
对于这个问题的解决,可以调用get()的重载,get(longtimeout, TimeUnit unit)。设置等待的时长,如果超时则抛出TimeoutException。
使用示例如下:
public class FutureAsyncDemo {
static Random random = new Random();
static ExecutorService executor =
Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//接收文章名称,获取并计算文章分数
public static int
getArticleScore(String aname){
Future<Integer> futureA =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreA());
Future<Integer> futureB =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreB());
Future<Integer> futureC =
executor.submit(new
CalculateArticleScoreC());
doSomeThingElse();
Integer a = 0;
try {
a = futureA.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureA.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer b = 0;
try {
b = futureB.get(3L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureB.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer c = 0;
try {
c = futureC.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
futureC.cancel(true);
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
return a+b+c;
}
private static void doSomeThingElse() {
System.out.println("exec other
things");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(getArticleScore("demo")
);
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreA implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
{
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().
getName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreB implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
{
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().
getName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}
class CalculateArticleScoreC implements
Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception
{
Random random = new Random();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(30);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().
getName());
return random.nextInt(100);
}
}在上述方法中,对于B的get()设置了超时时间三秒钟,如果当调用其获取返回值时,如果超过三秒仍然没有返回结果,则抛出超时异常,接着方法会再次向下运行。
对于Future来说,它能够支持任务并发执行,对于任务结果的获取顺序是按照提交的顺序获取,在使用的过程中建议通过CPU高速轮询的方式获取任务结果,但这种方式比较耗费资源。不建议使用
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。
相关文章

关于mybatis-plus-generator的简单使用示例详解
在springboot项目中集成mybatis-plus是很方便开发的,最近看了一下plus的文档,简单用一下它的代码生成器,接下来通过实例代码讲解关于mybatis-plus-generator的简单使用,感兴趣的朋友跟随小编一起看看吧2024-03-03
SpringBoot集成Aviator实现参数校验的示例代码
在实际开发中,参数校验是保障系统稳定和数据可靠性的重要措施,Aviator 是一个高性能的表达式引擎,它能够简化复杂的逻辑判断并提升参数校验的灵活性,本文将介绍如何在 Spring Boot 中集成 Aviator,并利用它来实现灵活的参数校验,需要的朋友可以参考下2025-02-02
基于@MapperScan和@ComponentScan的使用区别
这篇文章主要介绍了@MapperScan和@ComponentScan的使用区别,具有很好的参考价值,希望对大家有所帮助。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教2021-09-09












最新评论